Vitamin C is best known for its role in strengthening the immune system. But as a powerful antioxidant, it has many other important functions. Vitamin C is available in a variety of fruits and vegetables, beyond just your daily glass of orange juice. Continue reading for the 20 best food sources of Vitamin C to ensure you’re getting enough.
Vitamin C and Health
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that helps to neutralize free radicals throughout the body, which can otherwise cause damage to our cells. It also plays a role in making collagen, a fiber-like protein used to form connective tissues throughout the body. In addition, vitamin C plays a key role in wound healing, bone health, and iron absorption.
Vitamin C’s best-known function is its role in the immune system. Adequate intakes of vitamin C are important for proper immune function, though research findings investigating vitamin C supplementation and prevention of viruses such as the common cold have been inconsistent. While large doses of vitamin C may not prevent illness, there is some evidence that larger doses of vitamin C may decrease the duration and/or severity of the common cold in some populations.
Vitamin C Deficiency and Symptoms
Severe vitamin C deficiency is rare in developed countries. When severe deficiency does occur, it can lead to a disease called Scurvy. Symptoms of Scurvy include follicular hyperkeratosis (keratin buildup around hair follicles causing bumps on the skin), petechiae (small round spots that appear on the skin due to bleeding), bleeding gums, fluid accumulation in the joints, and shortness of breath.
In less severe forms of vitamin C deficiency, symptoms may include rough and dry skin, inflammation of the gums, decreased wound healing, and impaired ability to fight infection.
How Much Vitamin C Do We Get in Our Diet Each Day?
In the 2012 Canadian Community Health Measures Survey, vitamin C levels were reported as adequate among the majority of adults ranging from 20-79 years of age, and less than 3% of Canadian adults were found to have a vitamin C deficiency. Though deficiency is rare overall, deficiency is more common in those with a low fruit and vegetable intake, and those who smoke.
How Much Vitamin C Do We Need Each Day?
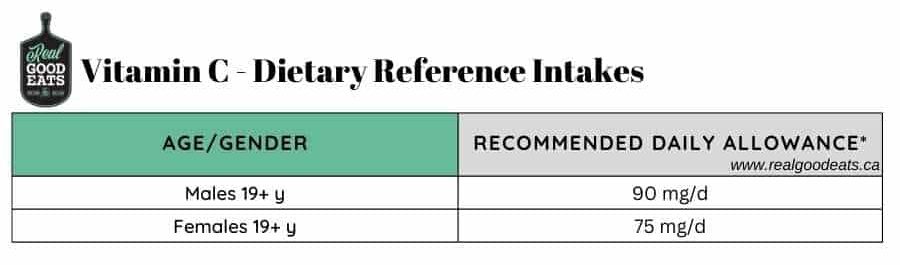
Vitamin C is an essential vitamin as it cannot be produced by the human body. It is water-soluble and does not get stored in the body, so it is important to get enough each day from foods to maintain adequate levels. The Recommended Daily Allowance in Canada is 90mg per day in adult males and 75mg per day in adult females.
Can We Get Enough Vitamin C From Food Only?
Vitamin C is widely available in fruits and vegetables, so it is certainly possible to get enough vitamin C from foods without the use of supplements or even your daily glass of orange juice. Continue reading for the 20 best food sources of vitamin C.
Best Food Sources of Vitamin
1. Yellow Bell Pepper

Yellow bell peppers contain 144mg of vitamin C per 1/2 cup serving. Include sliced raw yellow bell pepper snack with your favourite dip, roast in the oven as a side dish, or add to a stir fry or salad.
2. Red Bell Pepper

Red bell peppers contain 100mg of vitamin C per 1/2 cup serving. Include sliced raw red bell pepper snack with your favourite dip, roast in the oven as a side dish, or add to a stir fry or salad.
3. Kiwi

One kiwi contains 90mg of vitamin C. Enjoy kiwi on its own as a snack, include it in smoothies, or use it as a topping for yogurt.
4. Mustard Greens

Mustard greens contain 82mg of vitamin C per 1 cup serving. Add mustard greens to a salad, a smoothie, soup, stew, or stir-fry.
5. Kale

Kale contains 80mg of vitamin C per 1 cup serving. Sautee kale to include as a side dish, or add raw kale to salads, smoothies, or soups. Looking for recipe inspiration? Try our 20-Minute Garlicky Shrimp and Kale Gnocchi or our other favourite Dinner Recipes Using Kale.
6. Orange

A medium orange contains 70mg of vitamin C. Enjoy alone as a snack or with yogurt for a citrusy parfait.
7. Green bell pepper

Green peppers contain 63mg of vitamin C per 1/2 cup. Add to pasta, stir fry, chili, or use them to make stuffed peppers.
8. Pomelo

A 1/2 cup serving of Pomelo contains 61mg of vitamin C. Enjoy on its own or swap in for other citrus fruit in recipes.
9. Strawberries

Strawberries contain 50mg of vitamin C per 1/2 cup. Enjoy as a snack, use as a topping with oatmeal or yogurt, or blend into a smoothie.
10. Grapefruit

Grapefruit contains 47mg of vitamin C per 1/2 fruit. Enjoy alone as a snack or swap in for citrus fruit in recipes.
11. Papaya

A 1/2 cup serving of papaya contains 45mg of vitamin C. Enjoy alone or add to salads and smoothies.
12. Broccoli

Broccoli contains 42mg of vitamin C per 1/2 cup. Include as a side dish steamed, have raw with dip, or saute and add to pasta.
13. Pineapple

Pineapple contains 42mg of vitamin C per 1/2 cup serving. Enjoy alone as a snack, use in salsa, or grill with seasoning as a side dish.
14. Peas

A 1/2 cup serving of green peas contains 41mg of vitamin C. Enjoy cooked as a side dish or added to pastas or casseroles.
15. Brussels Sprout

Brussels Sprouts contain 40mg of vitamin C per 1/2 cup serving. Enjoy roasted with olive oil, salt and pepper, or shred raw Brussels to add to salads.
16. Edamame

Edamame contains 39mg of vitamin C per 1/2 cup serving. Enjoy steamed edamame as a high-protein snack or add to stir fry or salads as a plant-based protein source.
17. Clementine

Clementines contain 36mg of vitamin C per 1 fruit. Enjoy alone as a snack or add to salad.
18. Mango

A 1/2 cup serving of mango provides 32mg of vitamin C. Enjoy alone as a snack or add to salsa or tacos.
19. Cantaloupe

Coltaloupe contains 31mg of vitamin C per 1/2 cup. Enjoy alone as a snack, as part of a fruit salad or in smoothies.
20. Cauliflower

A 1/2 cup serving of cauliflower provides 27mg of vitamin C. Enjoy roasted as a side dish, shred and add to rice dishes for a hidden veggie, or have raw with dip.
Be sure to check out our free download that includes the top 20 Best Food Sources of Vitamin C (preview at the top of the post). You can access it here!
Related Posts
Sources
- Canada, H. (2010, November 29). Government of Canada. Canada.ca. Retrieved March 29, 2023, from https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/food-nutrition/healthy-eating/dietary-reference-intakes/tables/reference-values-vitamins-dietary-reference-intakes-tables-2005.html
- Institute of Medicine (US) Panel on Dietary Antioxidants and Related Compounds. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2000. 5, Vitamin C. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK225480/
- Government of Canada, S. C. (2017, July 12). Health reports vitamin C status of Canadian adults: Findings from the 2012/2013 Canadian health measures SurveyHealth reports vitamin C status of Canadian adults: Findings from the 2012/2013 Canadian health measures survey. Vitamin C status of Canadian adults: Findings from the 2012/2013 Canadian Health Measures Survey. Retrieved March 28, 2023, from https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/82-003-x/2016005/article/14612-eng.htm
- Douglas RM, Hemila H, Chalker E, Treacy B. Vitamin C for preventing and treating the common cold. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007:CD000980.


